Repositories
When you create a new cluster with Kubefirst, two new repositories will be added to your organization's GitHub account as shown here.
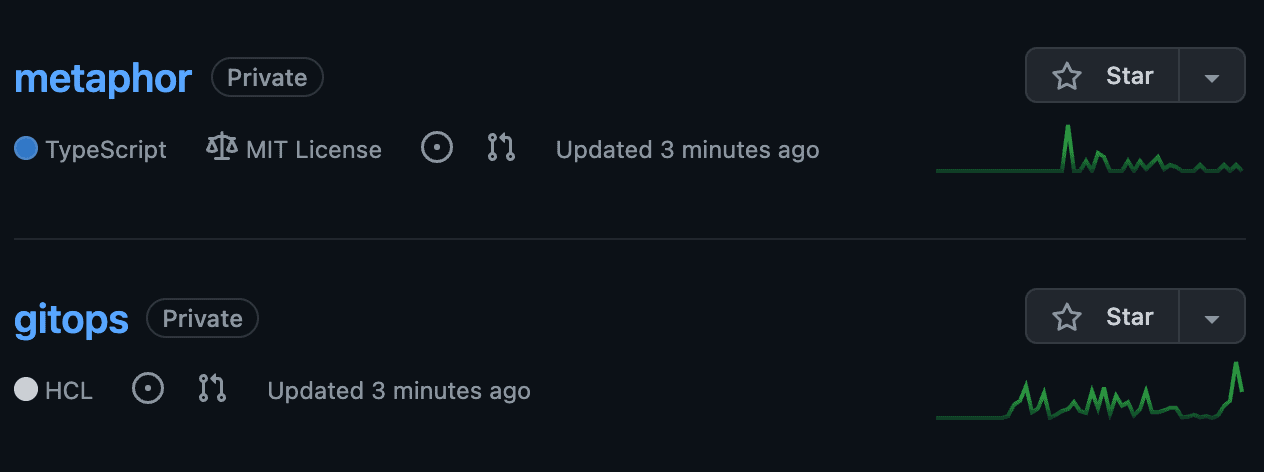
Repository Summary
gitops
The gitops repository houses all of our IAC and all our GitOps configurations. All of the infrastructure that you receive with Kubefirst was produced by some combination of Terraform and Argo CD. You can modify, update or add anything to this gitops repository based on your business needs: it is now yours.
The repository doesn't have any branch protection by default. We highly suggest that you add some on the main branch.
metaphor
The metaphor repository is an example application with source code, builds, and GitOps delivery used to showcase various features, integrations, and best practices of the Kubefirst platform. More details in the Metaphor documentation page.
GitHub Repository Management
These GitHub repositories are being managed in Terraform.
As you need additional GitHub repositories, just add a new section of Terraform code to terraform/github/repos.tf:
# set auto_init to false if importing an existing repository
# true if it's a new repository
module "your_repo_name" {
source = "./modules/repository"
visibility = "private"
repo_name = "your-repo-name"
archive_on_destroy = true
auto_init = false
}
GitHub's Terraform provider provides many more configuration options than just these settings. Check them out and add to your default settings once you're comfortable with the platform.
Take a look at the Resources section of the GitHub provider documentation.
That was just GitHub. Take a look at all the Terraform providers that are available; the list of technologies you can manage in Terraform is really impressive.
Making Terraform Changes
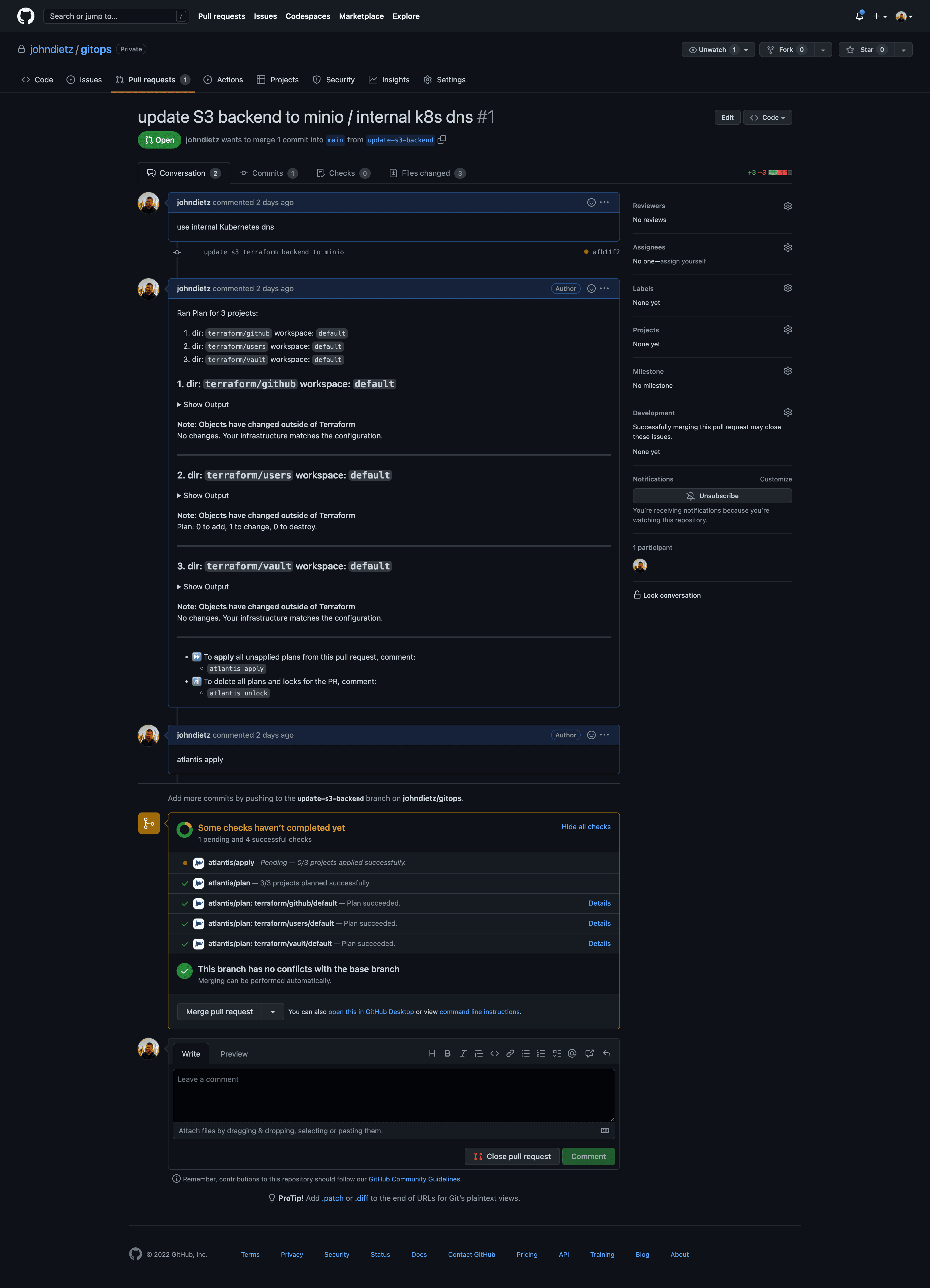
To make infrastructure and configuration changes with Terraform, simply open a pull request against any of the Terraform directory folders in the gitops repository. Your pull request will automatically provide plans, state locks, and applies, and even comment in the merge request itself. You'll have a simple, peer reviewable, auditable changelog of all infrastructure and configuration changes.
In the GitOps nature, we rely on repositories to have a single source of truth when it comes to project updates. Kubefirst makes heavy use of the GitOps approach to automate the development and maintenance of applications. In that regard, during the installation process, Kubefirst will create a few GitLab repositories as described below.
Repositories
gitops
The gitops repository houses all of our IAC and all of our GitOps configurations. All of the infrastructure that you receive with Kubefirst was produced by Terraform and all of your applications are delivered with Argo CD. You can modify, update or add anything to this gitops repository based on your business needs: it is now yours.
The repository doesn't have any branch protection by default. We highly suggest that you add some on the main branch.
metaphor
The metaphor repository is an example application with source code, builds, and GitOps delivery used to showcase various features, integrations, and best practices of the Kubefirst platform. More details in the Metaphor documentation page.
Repositories Management
The repositories are being managed in Terraform. If you need additional repositories, just add a new section of Terraform code to terraform/gitlab/kubefirst-repos.tf
module "your_repo_name" {
depends_on = [
gitlab_group.kubefirst
]
source = "./templates/gitlab-repo"
group_name = gitlab_group.kubefirst.id
repo_name = "your-repo-name"
create_ecr = true
initialize_with_readme = true
only_allow_merge_if_pipeline_succeeds = false
remove_source_branch_after_merge = true
}
GitLab's Terraform provider offer many more configuration options than just these settings. Take a look at the Resources section of the GitLab provider documentation.
Making Terraform Changes
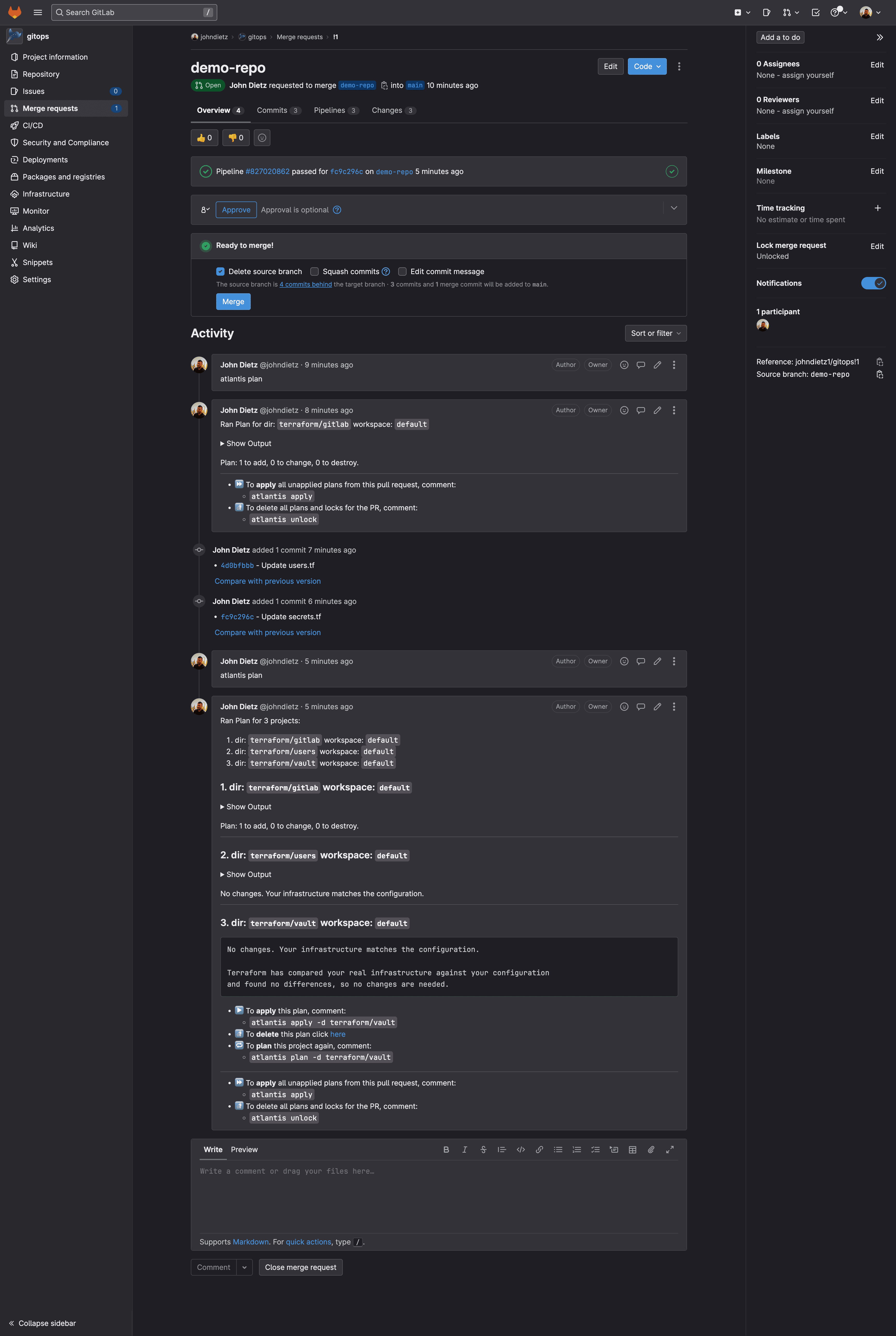
To make infrastructure and configuration changes with Terraform, simply open a merge request in the gitops repository. Your merge request will automatically provide plans, state locks, and applies, and even comment in the merge request itself. You'll have a simple, peer reviewable, auditable changelog of all infrastructure and configuration changes.
All this automation is possible because of Atlantis. Atlantis is a tool that runs in your Kubernetes cluster and via a webhook, listens for merge requests in your gitops repository. When it detect a merge request, it will run terraform plan, and post the plan as a comment in the merge request. If the Terraform plan succeed, Atlantis will run terraform apply, and post the results as a comment in the merge request.
 Please change your Homebrew tap by running
Please change your Homebrew tap by running